Environment Variables
Overview
ATAC allows you to manage and use environment variables through .env files. These environment variables enable you to configure various settings and parameters dynamically, enhancing flexibility and ease of use.
Setting Up Environment Variables
Creating an Environment File
To define environment variables, create a .env.my_env_name file inside the app directory. Here’s an example of what an environment file might look like:
BASE_URL=https://httpbin.org
ID=15
FILE_NAME=Cargo.toml
Once you have created your environment file you can now load it using the following command.
# if you use the default app directory or the ATAC_MAIN_DIR environment variable (OS side)
atac
# or with -d <directory> - The directory that contains the .env.my_env_name file
atac -d <directory>
Using Environment Variables
To use these environment variables within your requests, reference them by writing {{my_variable_name}}. For example:
{{BASE_URL}}will be replaced byhttps://httpbin.org{{ID}}will be replaced by15{{FILE_NAME}}will be replaced byCargo.toml
Environment variables are available everywhere except collection name, request name and textual bodies (JSON, HTML, XML, ...).
Using Environment Variables in TUI
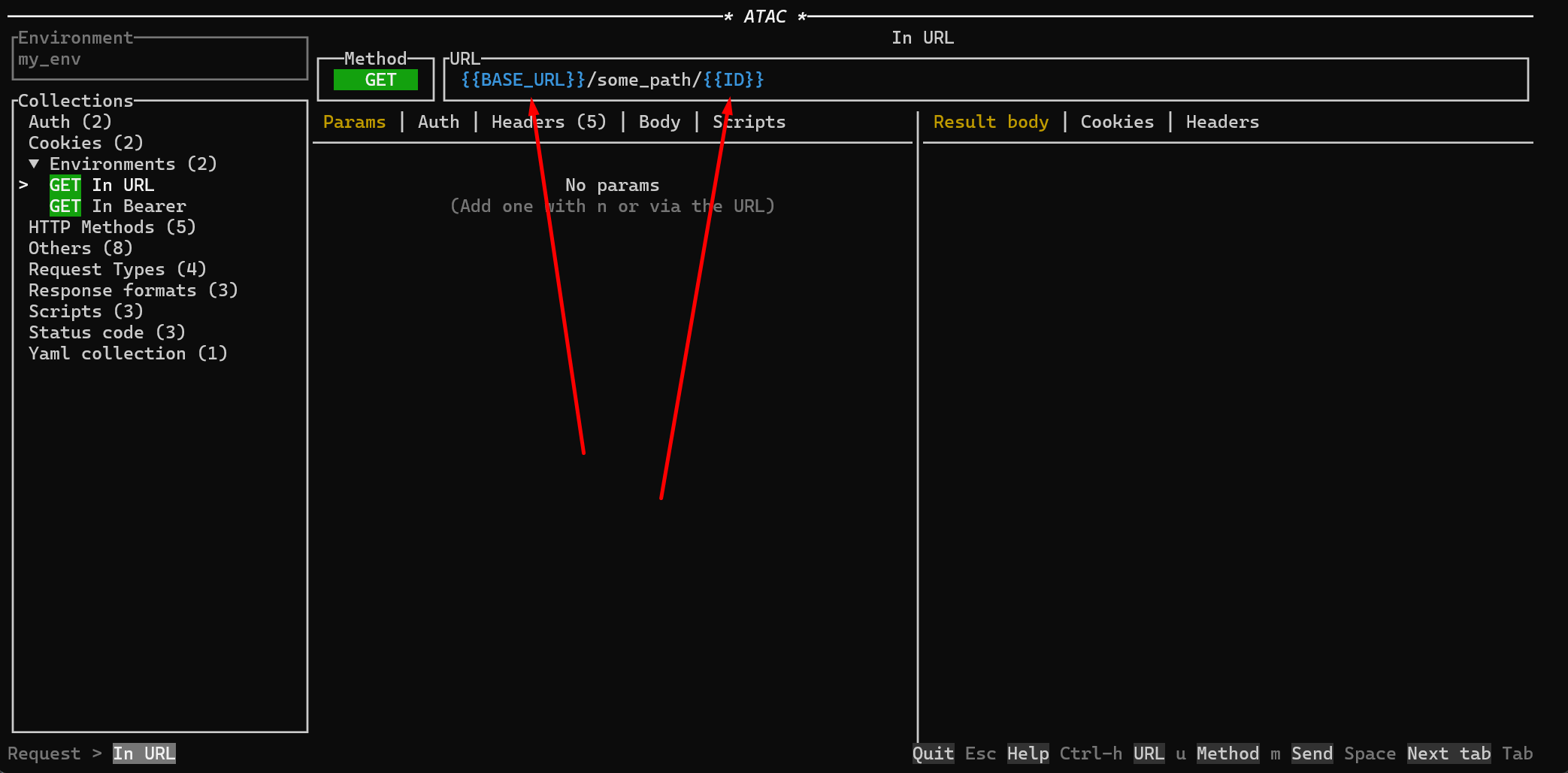
In the TUI, the name of the selected environment will appear in the top left gray box as follows:

When an environment variable from your selected environment is used in the request, it will be highlighted in blue, making it easy to identify and confirm.
Selecting an Environment
To select an environment in the TUI, ensure that your .env.my_env_name file is placed correctly in the app directory. The default key to change the selected environment is e, it will loop through the parsed .env files.
Using Environment Variables in CLI
In the CLI, you can specify which environment to use with the --env my_env_name parameter. This tells ATAC to use the environment variables defined in the .env.my_env_name file for the current session.
Example Usage
atac request my_collection/my_request send --env my_env_name
This command will load the environment variables from .env.my_env_name and make them available for use in your requests.